The rapid advancement of AI technologies has intensified global concerns regarding security vulnerabilities and ethical implications. While the broader international community demonstrates a predominant focus on securing AI systems against potential threats, the regulatory landscape, especially within the European Union, exhibits a notable emphasis on legislative measures such as the EU AI Act. With the AI Act, the EU is a trailblazer for AI regulations worldwide. Given the limited number of comparable regulations, the most interest into the AI Act is spread across the EU countries. However, also foreign companies that offer AI services in the EU need to engage in the AI Act. By analyzing search interest data from various regions, this article provides insights into how different stakeholders prioritize security versus regulation, setting the stage for informed policy discourse.
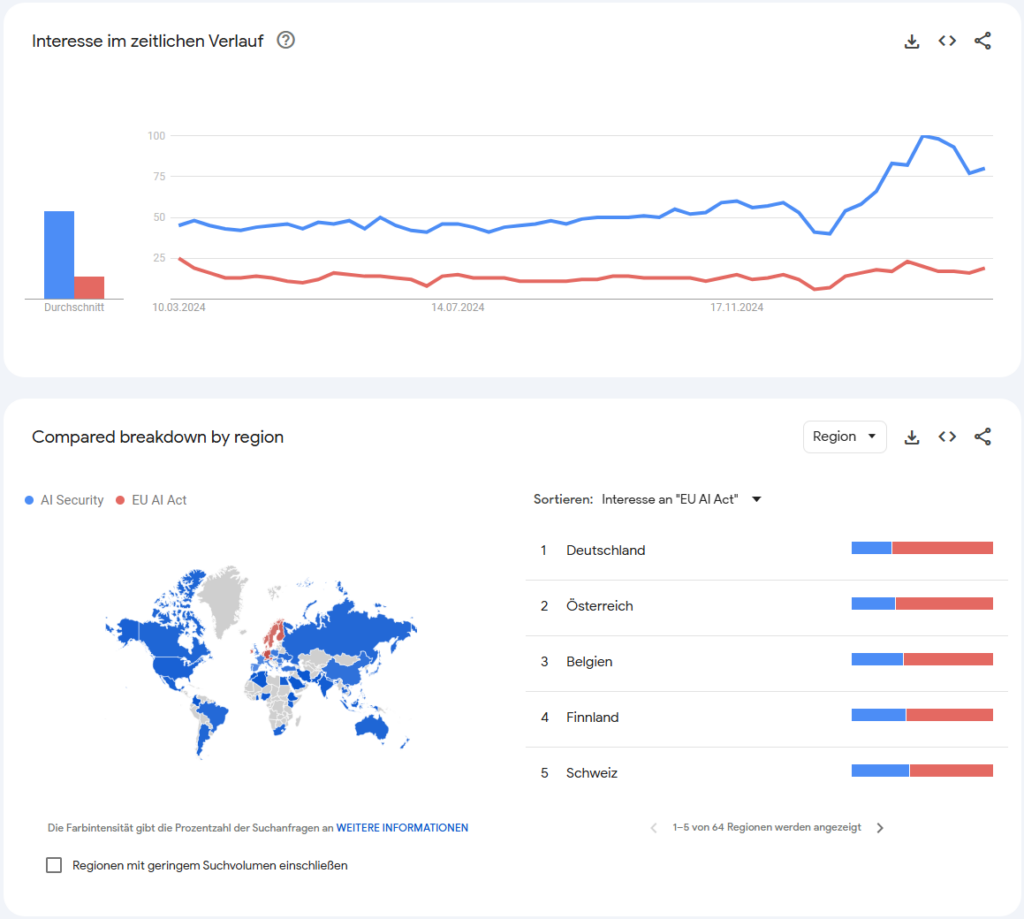
Google Trends Analysis
Notably, search data reveals that in most countries, the general public and industry stakeholders are more engaged in seeking information on securing AI systems than on understanding regulatory frameworks. The interest in “AI security” sees a significant raise while the EU AI Act only has a smaller increase in search interest.
Germany, however, emerges as an outlier within this trend; with 71% of its search interest focused on the EU AI Act, it significantly exceeds the worldwide average of 20% regulatory-related searches. In stark contrast, the United States exhibits a pronounced focus on AI security, with only 9% of search interest pertaining to the EU AI Act compared to 91% dedicated to AI security. Across the EU, there exists a near-equilibrium—approximately 50/50—between security and regulatory queries, with a distinct north-western regional emphasis on regulatory topics. These data points underscore the divergent priorities shaping the discourse on AI in different geopolitical landscapes.
Comparative Regional Analysis
The contrast between the United States and the European Union highlights significant regional differences in the approach to AI governance. In the US, the overwhelming focus on AI security suggests a prioritization of immediate technical defenses and mitigation strategies against potential AI threats. This may reflect both a technological and market-driven culture, as well as an emphasis on innovation and self-regulation. Conversely, the EU’s balanced search interest indicates a policy debate, where equal attention is given to enhancing AI security and establishing comprehensive regulatory frameworks, such as the EU AI Act. Germany’s exceptional interest in regulation may stem from its robust tradition of governance and precautionary policymaking. Such disparities reveal that while the global community is predominantly concerned with the direct risks posed by AI, European stakeholders are equally engaged in shaping the regulatory environment to manage these risks effectively.
Policy Implications and Future Outlook
The observed divergence in search interests carries significant policy implications. Globally, the focus on securing AI systems reflects an urgent need to address the technical vulnerabilities and potential misuse of AI. In contrast, the EU’s heightened regulatory interest signals a proactive approach to preemptively manage these risks through comprehensive legislation. However, this regulatory focus may inadvertently overshadow the imperative for robust security measures, thereby creating a potential mismatch between policy intentions and technical realities. Policymakers must therefore strive for a balanced approach that integrates stringent security protocols with adaptive regulatory frameworks. Future research should explore the efficacy of such hybrid models and assess how cross-regional collaborations can bridge the gap between regulatory oversight and technological resilience, ensuring that the promise of AI is harnessed without compromising public safety. The observed trends also reflect the unequal digital market share between EU and US, where the US with the largest digital corporations drive the interest for AI security.
Conclusion
In summary, while the global community is largely preoccupied with the technical challenges of securing AI, the European context, exemplified by regions such as Germany, demonstrates a pronounced regulatory focus through instruments like the EU AI Act. This divergence not only underscores differing cultural and policy priorities but also raises critical questions about the optimal balance between regulation and security. As AI continues to evolve, it is imperative that policymakers and industry leaders collaboratively address both dimensions to foster an ecosystem where innovation thrives alongside robust safeguards.